- Zyrtec and Claritin are effective second-generation antihistamines that help relieve common allergy symptoms like sneezing, itchy eyes, and a runny nose.
- Despite their popularity, these medications may not fully address all allergy symptoms for everyone, and some individuals may experience mild side effects such as drowsiness or dry mouth.
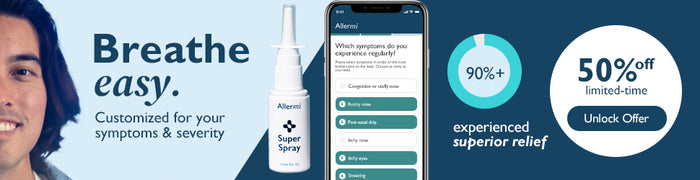
- Unlike standard antihistamines, Allermi is a nasal spray that combines antihistamines, micro-dosed decongestant, anti-discharge, and anti-inflammatory agents to target allergy symptoms more effectively because it treats the root cause.
Allergy season can be tough, with symptoms like sneezing, itchy eyes, and a runny nose getting in the way of daily life. Many people want an antihistamine that works well without making them feel sleepy.
Zyrtec and Claritin are both popular second-generation antihistamines that promise allergy relief with fewer sedative effects compared to older options. However, not everyone finds these medications to be the perfect fit for their needs.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at how Zyrtec and Claritin compare, including their benefits and potential drawbacks. We’ll also discuss an alternative option that could provide better relief for those who find these two antihistamines less effective.
Related: What to Do When Allergy Medicine Doesn't Work?
What is Zyrtec?
Zyrtec is an antihistamine used to relieve nasal symptoms such as sneezing, congestion, and a runny nose caused by allergies. Its active ingredient, cetirizine, works by blocking histamine to offer fast relief for allergy symptoms [*].
While Zyrtec is available in various forms, including chewable tablets, liquid gels, and syrup (for children), its most common form is a tablet. According to the website, this prescription-strength allergy medicine starts working within one hour.
This makes Zyrtec a popular choice for those seeking effective allergy symptom management.
What is Claritin?
Claritin is a non-drowsy antihistamine that contains loratadine, which blocks histamine, the chemical that causes allergy symptoms. It helps relieve sneezing, runny nose, and itchy or watery eyes, which is an option for allergy relief without causing sleepiness. Loratadine is long-acting, meaning it also provides extended relief throughout the day [*].
In addition to its standard tablet form, Claritin is available in several other formulations, including melt-in-your-mouth tablets, liquid-filled capsules, chewable tablets, and a cooling honey-flavored oral solution. These options make Claritin convenient and easy to take for various preferences.
Related: Benadryl vs. Claritin: Differences and Alternatives
Zyrtec vs. Claritin
To help you decide between Zyrtec and Claritin, we've prepared a table comparing key factors such as their indications, side effects, onset, duration, and more. This will give you a clear overview of how these two antihistamines stack up against each other.
| Zyrtec | Claritin | |
| Drug Class | Antihistamines | Antihistamines |
| Generic Name | Cetirizine | Loratadine |
| Indications | Temporarily relieves common allergy symptoms caused by hay fever, seasonal allergies, or other upper respiratory allergies. These include a runny nose, sneezing, itchy and watery eyes, as well as itching of the nose or throat. | Temporarily relieves such as sneezing, runny nose, itchy or watery eyes, and itchy nose or throat, which are common in conditions like hay fever and seasonal allergies. |
| Side Effects | Common side effects include headache, dizziness, nausea, and dry mouth. Note that Zyrtec is a second-generation antihistamine, which typically causes fewer sedative effects than older antihistamines, although some people may still feel drowsy. Some individuals may also experience fatigue or an upset stomach. | Common side effects include headache, dry mouth, dizziness, fatigue, and nausea. While Claritin is designed to cause fewer sedative effects than older antihistamines, a small number of individuals may still experience mild drowsiness or other side effects. However, it is typically well-tolerated with minimal sedation. |
| Duration/Course | Relieves symptoms for a full 24 hours | Relieves symptoms for a full 24 hours |
| Onset | Starts working at 1 hour | Within 20 mins to 1 hour |
| Dosage | For adults and children 6 years and older: Take one 10 mg tablet once daily. Do not exceed one 10 mg tablet within 24 hours. For less severe symptoms, a 5 mg dose may be suitable. Always consult your doctor before use, especially if you have any pre-existing health conditions or concerns. | For adults and children 6 years and older: Take one 10 mg tablet once daily. Do not exceed one 10 mg tablet within 24 hours. Children under 6 years of age, as well as individuals with liver or kidney disease, should consult a doctor before using Claritin. |
| Drug Interaction | May interact with certain medications used for treating seizures, depression, or anxiety, such as carbamazepine or amitriptyline. Combining Zyrtec with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants, such as sedatives or tranquilizers, can enhance drowsiness and impair cognitive function. | Combining Claritin with certain antifungal medications, like ketoconazole, or antibiotics, such as erythromycin, may increase the levels of loratadine in the body, potentially leading to an increased risk of side effects. Drugs that affect liver enzymes, such as cimetidine, may interfere with how Claritin is metabolized. |
| Warnings/Precautions | Do not use it if you have ever had an allergic reaction to this product, any of its ingredients, or to antihistamines containing hydroxyzine. If you have liver or kidney disease, consult your doctor, as they may need to adjust your dose. If pregnant or breastfeeding, it’s recommended to consult a healthcare professional before using Zyrtec. | Do not use Claritin if you have ever had an allergic reaction to this product or any of its ingredients. Before using, consult a doctor if you have liver or kidney disease, as your doctor may need to adjust the dosage. When using this product, do not exceed the recommended dose, as taking more than directed may cause drowsiness. If pregnant or breastfeeding, it’s recommended to consult a healthcare professional before using Claritin. |
What’s the Best Alternative for Zyrtec and Claritin?
Allermi could be an ideal alternative. Unlike standard antihistamines like Zyrtec and Claritin, Allermi offers a more customized approach to nasal allergy symptoms, and treats the root cause, which is in the nose
Available in a nasal spray form, Allermi not only contains antihistamines but also includes other active ingredients, such as micro-dosed decongestant, anti-discharge, and anti-inflammatory agents. This combination makes Allermi particularly effective for individuals who may need more than one type of active ingredient to address their allergy symptoms.
The active ingredients in our nasal spray are adjusted to fit your specific profile to make sure that you're receiving exactly what you need for the best possible results. Plus, Allermi is backed by a team of allergists who work to ensure its effectiveness and safety.
Many users notice an initial improvement in their nasal symptoms within just 10-15 minutes, with continued relief over the following days and weeks (3-4 weeks).
It’s a more holistic and targeted approach to managing nasal allergies for those looking for a better solution.
Related: How Long Does It Take for Allergy Medicine to Work?
The Bottom Line
Zyrtec and Claritin have long been popular choices for allergy relief. Zyrtec, with its active ingredient cetirizine, and Claritin, with its active ingredient loradatine. Claritin is known for its non-drowsy formula. They’re a go-to for many seeking daytime allergy relief.
However, both of these medications may not always provide the level of symptom relief some individuals need. If you’ve found that Zyrtec or Claritin doesn’t fully address your allergy symptoms, Allermi could be the solution you're looking for.
Discover how Allermi can provide you with customized, effective allergy relief. Learn the science behind it today.
References:
- ScienceDirect. (n.d.). Cetirizine. ScienceDirect. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/cetirizine
- ScienceDirect. (n.d.). Loratadine. ScienceDirect. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/loratadine